

No. I think they both lose more than they gain here. It doesn’t make sense as a strategy. Ego clash is a simple explanation.


No. I think they both lose more than they gain here. It doesn’t make sense as a strategy. Ego clash is a simple explanation.
Too bad you don’t get to bring your equipment, but at least you will get to see them :D Good luck finding some wild ancestors!
Great find, congratulations!!
Enjoy your holidays!! 🕊️

Hi! I’ve looked through /r/shittyaskscience and I think it leans too far into jokes with very little actual science content. The idea behind mander is to support specific, niche science-related communities, so a general joke-focused community doesn’t really fit.
For ‘science_memes’, the mod is a very capable superstar and I agree with their vision of memes as a laid-back way to connect people to science. It’s plausible that a community like ‘shittyaskscience’ could achieve something similar, but honestly I think science_memes already covers that space well.
As for !askscience - it simply hasn’t been created yet. It would be more fitting than ‘shittyaskscience’, but I still prefer encouraging people to ask lichen questions in the lichen community, mushroom questions in the mushroom community, chemistry questions in the chemistry community, and so on. I support content flowing toward niche communities rather than having a centralized place for general questions. A general community would be more popular, but popularity isn’t a goal, and it works against the underlying philosophy. Niche spaces may be smaller, but they offer much better signal-to-noise for building meaningful connections.

Unfortunately the article is behind a paywall… But I am curious, does this mean there won’t be any new Cortex-Mxs microprocessors?
The summary says that Arm wants to “enter the chip design space”. They weren’t doing this already?
And, is the prospect of a proprietary chip an exciting tease when pitted against an open standard one? I am excited about RISC-V microprocessors precisely because they rely on an open standard, so I am curious to see what their angle here is. I tried to find a non-paywalled source but I couldn’t find one.


Solar Maximum happens every 11 years or so, right? I will keep paying attention!


Wow, that is spectacular!


Stay up until 3:30 the other night. When it exploded again it gave a giant middle finger to Europe:
Aahh, that’s rough 😅
But lo, the density died and the pillars are diffused. My friend caught a little bit on the horizon in camera. I saw a little bit of red but nothing stunning. Very faint. You can just see the pink on the horizon. This is facing north.
Nice! Is this your first time seeing it, or is this something that you get to attempt often?


I bought a National Instrument’s data acquisition card (PCIe-6535B) not knowing that National Instruments is not very Linux-friendly and I was not able to get it working. At least it was a used card so I did not pay to much for it, but I learned my lesson not to assume compatibility.
Once I also used ‘rm -rvf *’ from my home directory while SSH’d into a supercomputer (I made a syntax error when trying to cd into the folder that I actually wanted to delete). I was able to get my data restored from a backup, but sending that e-mail was a bit embarrassing 😆
Those remind me a bit of when we were putting colors and other stuff into dia frames and then projecting.
Possibly similar type of dynamics going on! I never tried this.
I used 99%. 70% will probably work too. I can test later and let you know.
Ahaha, after the 7th snooze finally got out of bed. Great photo!


Beautiful! Thanks for sharing!
When I saw it, I thought “this looks like it must be fluorescent under UV!”. So, I looked it up, and found out that it probably isn’t fluorescent (but if you have a UV flashlight to test, I am quite curious to know).
From what I can find, the yellowish green color comes from the molecule vulpinic acid. Especially interesting is that this molecule is prone to breaking down in the presence of light (terrible quality for a pigment), but a recent paper suggests that inside of the lichen the molecule sticks to polysaccharide chains in a way that dampens the molecule’s photogradation pathway. The pigment can still absorb UV light but rather than dissipating the energy in a destructive process the polysaccharide holds the molecule in place and dampens the molecule’s response by quickly dissipate the energy. Here is the open-access paper, and diagram below.

I also found that the name Vulpicida, Letharia vulpina, and Vulpinic acid come from folk tales about these lichens being used to poison foxes (vulpes = fox) and wolves. Not sure if it is true…
Apologize for the information dump, but I saw the bright colors and just had to look into its photophysics 😂
I continued playing with this concept. Turmeric resin extracted with isopropanol, and now I blended some beets with water and passed the blended liquid through a coffee filter to obtain the purple betains in water. Deposited as layers one on top of the other. Once dried, I added a drop of oil, and then one drop of soap. No baking soda this time.
It is quite fun to see these under the microscope. It looks like a living landscape, with mountains walking across and interacting with each other as turbulent particles whiz inside of them erratically.


You’ve still got time! Between 10pm and 2am are the golden hours for this sort of thing, but look north as it gets dark. Use your phone camera with a long exposure to check. :)
I’m living in Amsterdam at the moment, in a city environment. From what I have found, I would need to travel to the north of the Netherlands to have a good chance of seeing something. A difficult trip to improvise on a Sunday night. Hopefully when the next opportunity arises I will know enough to appreciate it more deeply.


Ahh cool! Actually it was one of that mod’s latest post that I had just read before making my flux rope comment 😆


Not intentional!
Took a bit of digging. The post was federated, but it showed up to me as “Removed by mod”:
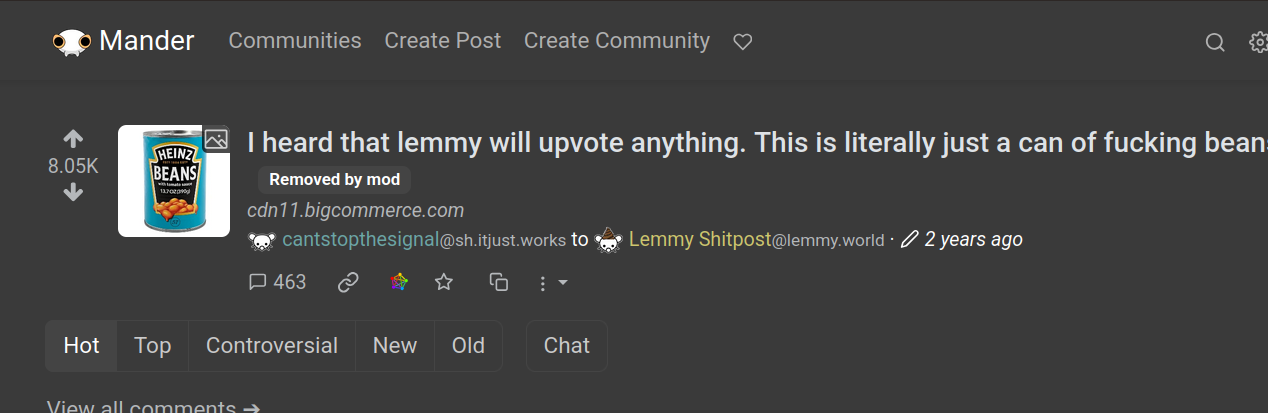
Looking through the post’s moderation history, I find that the user was banned from community and then unbanned. I also see some removed posts from that same author to that same community around that same time.
My guess is that the most was removed by mod, then restored, but only the removal federated through and not the restore.
I have manually restored it, so you should be able to find it now: https://mander.xyz/post/977581/19535554


Thanks a lot! I can understand some of what I am looking at now.
I would like to find out if there are associated phenomena that I might be able to notice using software-defined radio. Maybe some time I can chase after an aurora, but this time I am unprepared.






















You are pointing a UV lamp at it which probably sends out 365 nm or 395 nm photons. The lichen is shooting back photons with a broad range of wavelengths, and a lot of ~600 - 750 nm ones (red). So, the UV photons had to be “captured” by some molecular system, the system dissipated some energy, and then re-radiated some of these longer-wavelength photons.
The general term that covers the many different possibilities is “photoluminescence”. In this case we can say for sure that the lichen exhibits “UV-induced photoluminescence”, because it is re-emitting lower energy (longer-wavelength) photons. It is common to make the connection “photoluminescence” = “fluorescence”, but technically fluorescence makes specific claims about how the light is re-emitted (singlet -> singlet emission), and it is not the only luminescence process. Other examples of luminescence are phosphorescence from a triplet state and luminescence via charge-recombination. So, to call it “fluorescence” in the strict sense we need know what the exact pathway is.
That said, when it comes to biological pigments fluorescence is generally the most common pathway. Triplets that live long enough to produce light are generally undesirable as they can react indiscriminately with molecules inside of the cell as well as produce reactive oxygen species, and good phosphorescent materials often combine metals and heavy atoms that are not as abundant in living tissue.
So, knowing nothing else, and seeing that red light comes out when you shine UV/blue light on a lichen, it is generally fair to call it “fluorescence”.
Now, if we discuss this specific lichen… I have looked it up and it does get interesting! Do you have it with you? I suspect that its fluorescence might be different during the day than during the night.
I can find online two significant fluorescent components: parietin, which produces the fluorescent yellow pigment, and Chlorophyll a/b, which produces red fluorescence. There is an interesting paper exploring the idea that one functional purpose of parietin’s fluorescence is that it can transfer energy to the algae to boost their photosynthesis. Their conclusions in the paper is that the idea is not supported by the evidence, so, a “negative result”. It is a fun example of the type of research that is performed in photobiology and also an example to show that even negative results can be interesting enough to be published!
As for the difference between day and night - if what you see is a combination of the fluorescence of parietin and chlorophyll, then the color might change with the day/night cycle. Photosynthetic organisms regulate the flow of excess photon energy towards a safe non-radiative dissipation pathway in response to light. This is called the non-photochemical quenching pathway, and during the day this pathway tends to be active. During the night there is little light, and so this protective pathway shuts-off. This allows more of the absorbed photon energy to flow into the radiative fluorescence pathway, increasing the red fluorescence. You can actually see this easily with plants - you can dark adapt a leaf and then compare its fluorescence with that of a leaf that is being exposed to a bright light. The dark-adapted one will usually show significantly more red fluorescence.
This time you did ask, so I won’t apologize for my essay 😆 But I am a bit sorry I didn’t have the time to make it shorter.